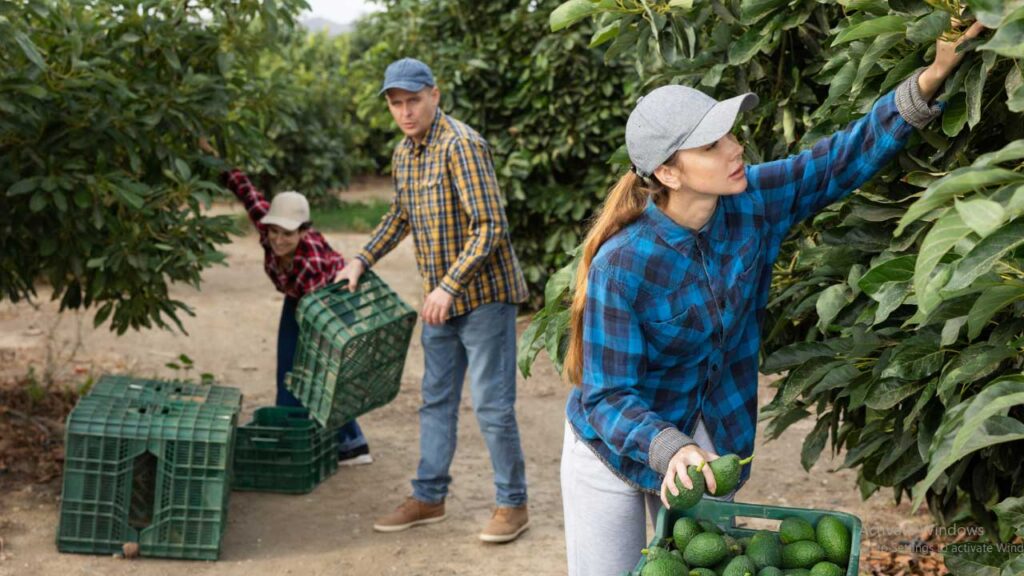
In today’s fast-paced world, where convenience often trumps nutritional value, the journey from seed to plate has never been more crucial for our health and wellness. Sustainable gardening offers a transformative approach, enriching our diets with fresh, nutrient-dense produce and fostering physical and mental well-being. This article discussess landscapes of sustainable gardening, exploring its profound implications for nutritional health and holistic wellness.
Cultivating Nutrient-Rich Bounty
Sustainable gardening is a paradigm that prioritizes environmental stewardship and biodiversity conservation while producing wholesome food. Unlike commercially produced fruits and vegetables, which may traverse vast distances and undergo chemical treatments, produce from sustainable gardens is harvested at peak ripeness, retaining maximum nutritional value.
Studies have shown that homegrown or locally sourced produce tends to be higher in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, offering a potent shield against chronic diseases and promoting overall vitality.
The Nutritional Edge of Freshness
The moment a fruit or vegetable is plucked from the vine, it begins to lose vital nutrients. This decline accelerates during transportation and storage, rendering store-bought produce less nutrient-dense by the time it reaches our plates.
In contrast, sustainable gardening ensures a swift transition from garden to table, preserving each harvest’s freshness and nutritional integrity. Individuals can capitalize on the full spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals essential for optimal health by consuming freshly picked produce.
Gardening for Wellness
Beyond its nutritional bounty, sustainable gardening cultivates a profound connection between individuals and the natural world, fostering holistic wellness. Engaging in gardening activities, whether sowing seeds, tending to plants, or harvesting fruits, offers a myriad of physical and mental health benefits.
The therapeutic effects of gardening are well-documented, with studies highlighting its role in reducing stress, alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety, and promoting a sense of accomplishment and purpose.
Stress Reduction and Immune Support
The rhythmic motions of gardening, from digging soil to watering plants, promote relaxation and mindfulness, effectively reducing stress levels. Exposure to green spaces and sunlight during gardening activities enhances vitamin D synthesis, bolstering immune function and resilience against infections and diseases.
Moreover, the act of nurturing living organisms instills a sense of responsibility and connection, fostering emotional well-being and social cohesion within communities.
Cultivating Physical Vitality
Sustainable gardening is inherently physical, offering a low-impact form of exercise accessible to individuals of all ages and abilities. Digging, weeding, and lifting bags of soil or compost engage various muscle groups, improving strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health.
Gardening also encourages outdoor activity, promoting vitamin D absorption and supporting bone health. Studies have shown that regular gardening can effectively contribute to weight management and reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases.
Enhancing Mental Clarity and Resilience
The sensory experience of gardening, from the earthy scent of soil to the vibrant colors of blooming flowers, stimulates cognitive function and emotional well-being. Engaging in repetitive tasks, such as pruning or harvesting, induces a meditative state, quieting the mind and fostering mental clarity.
Moreover, witnessing the growth and transformation of plants instills a sense of hope and resilience, reminding individuals of the cyclical nature of life and the power of nurturing living beings.
The Advantage of Homegrown Harvests
One of the often overlooked advantages of sourcing fruits and vegetables from sustainable gardens is the ability to harvest them at peak ripeness.
Unlike store-bought produce, which is often picked prematurely to withstand transportation and prolong shelf life, homegrown crops can fully mature on the vine, bush, or tree. This extended ripening period not only enhances the flavor and texture of the produce but also maximizes its nutritional content.
The Ripening Process and Nutrient Development
As fruits and vegetables ripen, they undergo a series of biochemical changes that contribute to their sensory attributes and nutritional profile.
During ripening, the levels of certain vitamins, such as vitamin C and beta-carotene, may increase, while others, like vitamin B and certain minerals, may remain stable or decrease slightly. However, the overall nutrient density of the produce tends to peak at optimal ripeness, making freshly harvested fruits and vegetables from sustainable gardens potent sources of essential nutrients.
Enhanced Flavor and Palatability
The ripening process is closely linked to the development of flavor compounds, sugars, and aromatic compounds within fruits and vegetables. As produce ripens on the plant, sugars accumulate, acidity decreases, and complex flavors emerge, resulting in a more vibrant and satisfying culinary experience.
Homegrown tomatoes, for example, are renowned for their rich, sweet flavor when allowed to ripen fully on the vine, surpassing the taste of their commercially produced counterparts.
Nutritional Impact of Ripeness
Research indicates that fruits and vegetables harvested at peak ripeness may contain higher levels of antioxidants, phytochemicals, and other bioactive compounds compared to those harvested prematurely.
For instance, studies have shown that fully ripe tomatoes exhibit greater concentrations of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant associated with numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease and certain cancers.
Practical Tips for Optimal Ripening
To harness homegrown produce’s full nutritional and sensory potential, it’s essential to understand the ripening process and employ strategies to promote optimal ripeness.
This may involve monitoring the color, texture, and aroma of fruits and vegetables and harvesting them at the peak of ripeness. Additionally, allowing produce to ripen further after harvest, under controlled conditions, can enhance its flavor and nutritional value.
Community Connections and Food Security
Sustainable gardening transcends individual benefits, serving as a catalyst for community engagement and empowerment. Community gardens provide access to fresh, locally grown produce and foster social connections, knowledge sharing, and collective resilience.
By promoting food sovereignty and self-reliance, sustainable gardening initiatives contribute to greater food security, mitigating the impact of food deserts and systemic inequalities.
Cultivating a Sustainable Future
In an era marked by environmental degradation and climate uncertainty, sustainable gardening emerges as a beacon of hope, offering practical solutions to global challenges. Individuals can mitigate their ecological footprint by adopting regenerative practices such as composting, rainwater harvesting, and biodiversity conservation while enhancing food security and resilience.
Through collective action and advocacy, sustainable gardening movements have the potential to catalyze broader shifts toward a more equitable, nourishing, and sustainable food system.
Sustainable gardening is like a full-circle journey, feeding us fresh food while also feeding our spirits and the Earth. Hence, with taking care for our gardens, we’re not just growing veggies but also growing resilience and connection to nature, finding peace and renewal along the way.

Lifebing is driven by an unrelenting passion for promoting health and well-being, our team is wholly committed to curating exceptional content and immersive experiences.