Choline benefits your body in ways you might not expect, yet most Americans don’t get enough of this important nutrient that supports brain health, liver function, and muscle movement.

What Is Choline and Why Do You Need It?
Choline is a nutrient your body needs to work properly. Think of it as fuel for your brain and muscles. Your body makes small amounts of choline, but you need to get most of it from food.
This nutrient helps build cell membranes, which are like walls around your cells. It also helps your brain send messages to other parts of your body. Without enough choline, your body can’t function at its best.
The Institute of Medicine says adult men need 550 mg of choline daily, while adult women need 425 mg. Pregnant women need even more at 450 mg, and breastfeeding mothers need 550 mg.
Brain Health and Memory Support
Your brain loves choline. This nutrient helps make a chemical called acetylcholine, which acts like a messenger in your brain. This messenger helps you:
- Remember things better
- Focus on tasks
- Learn new information
- Think clearly
Studies show that people who eat more choline-rich foods often have better memory skills. Your brain uses choline to build new connections between brain cells. These connections help you store and recall memories.
Choline also protects your brain as you age. Getting enough of this nutrient may help keep your mind sharp and reduce the risk of memory problems later in life.
Anti-aging benefits
Choline also ties into anti-aging supplements. Along with nutrients like L-carnitine and TMG (trimethylglycine), it supports healthy aging by protecting brain cells, improving mitochondrial energy, and lowering homocysteine levels. This combination may help reduce age-related memory decline and support long-term brain health.
Liver Function and Fat Processing
Your liver works hard every day to clean your blood and process nutrients. Choline helps your liver do these important jobs. Here’s how:
Fat Transport: Choline helps move fats out of your liver. Without enough choline, fats can build up in your liver, which isn’t healthy.
Detoxification: Your liver uses choline to help remove harmful substances from your body. This process keeps your blood clean and your body healthy.
Metabolism Support: Choline helps your liver break down fats and cholesterol. This process helps keep your cholesterol levels in a healthy range.
People who don’t get enough choline may develop fatty liver disease. This condition happens when too much fat builds up in the liver, making it harder for the organ to work properly.
Because choline helps your liver process fats, it can also play a role in appetite regulation. Some studies suggest that when your body metabolizes fats more efficiently, you may feel fuller for longer, helping reduce appetite naturally.
Muscle Movement and Athletic Performance
Every time you move, your muscles need choline to work correctly. This nutrient helps your brain send signals to your muscles telling them when and how to move.
Athletes often benefit from getting enough choline because it supports:
- Muscle coordination
- Reaction time
- Endurance during exercise
- Recovery after workouts
Research shows that intense exercise can lower choline levels in your body. If you’re very active, you might need more choline than the average person to keep your muscles working well.
Magnesium Benefits
Choline works hand in hand with minerals like magnesium. Magnesium deficiency can cause muscle cramps, fatigue, and slower recovery, while magnesium bisglycinate supplements are often recommended for athletes to improve endurance and relaxation. Pairing adequate magnesium with choline ensures your muscles fire and recover properly.
Pregnancy and Baby Development
Pregnant women need extra choline for good reason. This nutrient plays a key role in helping babies develop properly. During pregnancy, choline supports:
Brain Development: Choline helps build your baby’s brain and nervous system. Getting enough during pregnancy may help your child have better memory and learning skills throughout life.
Spinal Cord Formation: This nutrient helps prevent birth defects of the brain and spinal cord, similar to how folic acid works.
Cell Growth: Choline helps cells divide and grow properly, which is crucial during rapid baby development.
Many prenatal vitamins don’t contain enough choline, so pregnant women often need to focus on eating choline-rich foods or taking additional supplements.
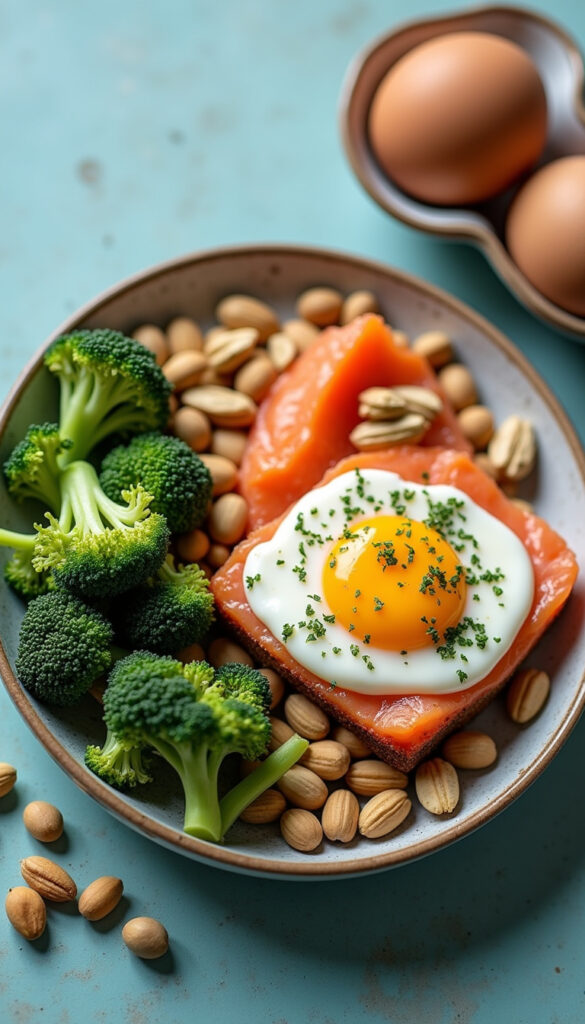
Best Food Sources of Choline
You can find choline in many common foods. The best sources include:
Animal Products:
- Eggs (especially egg yolks)
- Beef liver
- Chicken
- Fish like salmon and cod
- Milk and yogurt
Plant Foods:
- Soybeans
- Quinoa
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Peanuts and almonds
Other Sources:
- Wheat germ
- Navy beans
- Shiitake mushrooms
Eggs are one of the richest sources of choline. Just one large egg contains about 147 mg of choline. Beef liver tops the list with over 400 mg per serving, but most people prefer eggs as a daily source.
Signs You Might Need More Choline
Your body gives you signals when you’re not getting enough choline. Watch for these signs:
- Memory problems or brain fog
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue that doesn’t go away with rest
- Mood changes
- Liver problems
If you notice these symptoms, talk to your doctor. They can help figure out if low choline might be the cause and suggest ways to get more of this important nutrient.
How to Add More Choline to Your Diet
Getting enough choline doesn’t have to be hard. Try these simple tips:
Start Your Day Right: Eat eggs for breakfast. Two eggs give you about 294 mg of choline.
Choose Organ Meats: If you like liver, add it to your meals once or twice a week.
Snack Smart: Choose nuts like almonds or peanuts for a choline boost.
Add Vegetables: Include broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and other cruciferous vegetables in your meals.
Try Plant Proteins: Eat more soybeans, quinoa, and beans.
Choline Supplements: What You Should Know
Most people can get enough choline from food, but some might benefit from supplements. This includes:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- People who don’t eat eggs or meat
- Athletes who train intensively
- Older adults with memory concerns
If you’re thinking about taking choline supplements, talk to your healthcare provider first. They can help you decide if you need them and what dose might be right for you.
Balancing Choline with Other Nutrients
Choline works best when you get it as part of a balanced diet. It works together with other nutrients like:
- Folate (vitamin B9)
- Vitamin B12
- Omega-3 fatty acids
These nutrients support many of the same body functions as choline. Getting all of them helps your body work at its best.
Related Nutrients and Hacks
If you’re following diets like Paleo, you may already be eating more eggs, fish, and organ meats – all rich in choline. Paleo hacks often emphasize nutrient-dense foods that naturally boost choline and magnesium levels. Combining these strategies can maximize energy, support your metabolism, and help keep your brain sharp.